Heat Shrink Kits, also known as Splice Kits, are electrically insulated and protect wires and electrical components. Heat shrink tubing is designed to insulate wires, providing abrasion resistance and protection from environmental harm for stranded and solid wire conductors, joints, and connections in electrical engineering.
In this blog, we’ll go over how heat shrink tubing works, and different parts of a Heat Shrink Kit. To learn how to install a Heat Shrink Kit, check out our blog What the Heck are Heat Shrink Kits?
What's in a heat shrink kit?
The average Heat Shrink Kit consists of heat shrink tubes and stakons. Boshart's Heat Shrink Kits range from as small as 2 heat shrink tubes and stakons to as large as 12 heat shrink tubes and stakons.
Click here to see all of Boshart’s Heat Shrink Kits.
How Does it work?
Heat shrink tubing is mechanically expanded plastic tubing that holds the expanded diameter until it’s heated. Once heated, the tubing will return to its original diameter. Heat Shrink Kits work by creating a seal that prevents liquid and solid contaminants from accessing sensitive components.
Black Vs. Clear Heat Shrink Kits
 Black Heat Shrink Kits should be used to make splices in all above ground electrical cable splicing applications. These are ideal for above ground applications since black heat shrink tubing is flame retardant, due to its carbon content.
Black Heat Shrink Kits should be used to make splices in all above ground electrical cable splicing applications. These are ideal for above ground applications since black heat shrink tubing is flame retardant, due to its carbon content.
Clear Heat Shrink Kits are commonly used in making power cable splices to submersible water pump motors. The clear tubing is ideal for this application because it lets the installer see the flow of the adhesive while shrinking the tube. This helps ensure there are no air pockets that could jeopardize the watertight seal.
Choosing the Right Size
Choosing the right heat shrink tubing size is done by considering two key dimensions, the Expanded I.D. and the Recovered I.D. The Expanded I.D. is the minimum internal diameter of heat shrink tubing before heat is applied for recovery. The Recovered I.D. is the internal diameter of heat shrink tubing after being allowed to recover fully. You will use these dimensions to find the largest diameter and smallest diameter needed.
Largest Diameter
The first step in choosing the right size is to determine the largest section on the parts you are covering with tubing. Then, use a caliper or a ruler to measure the diameter. Once you have this measurement, you want to choose heat shrink tubing that has an Expanded I.D. that is 20% to 30% bigger than your largest measurement. The extra 20% to 30% will allow room to slide the expanded tubing over the largest part you’re trying to cover.
Smallest Diameter
Using your caliper or ruler again, measure the smallest part you are covering with tubing. Then check that the heat shrink tubing has a high enough shrink ratio to get a snug fit once it has reached its Recovered I.D.
Choosing the AMOUNT of Heat Shrink Tubes
When buying a Heat Shrink Kit, the kit will show the total number of heat shrink tubes included. These are used for both the conductors and the ground wire. For a two wire pump, you will require three heat shrink tubes and stakon connectors. For a three wire pump, you will require four heat shrink tubes and stakon connectors.
3:1 vs. 4:1 Shrink Ratio
Heat shrink kits come in a 3:1 or 4:1 shrink ratio. Although similar, one of these sizes will be better suited for your application.
3:1
With a 3:1 Heat Shrink Kit, the tubing will be one-third the original size once heat is applied. The main advantage of a 3:1 Heat Shrink Kit is that the tubing has a greater material mass which provides a thicker wall for added abrasion protection. A disadvantage of the 3:1 Heat Shrink Kit is that they take more heat and time to get the material to “shrink” temperature, making them more difficult to shrink down to the Recovered I.D. in certain conditions.
4:1
With a 4:1 Heat Shrink Kit, the tubing will be one-fourth the original size once heat is applied. The main advantage of a 4:1 Heat Shrink Kit is that the tubing shrinks down to the Recovered I.D. very quickly due to the decreased material and thinner wall thickness. A disadvantage to the 4:1 Heat Shrink Kit is that they have less material mass which provides a thinner wall and less abrasion protection.
MOST POPULAR heat shrink Kits OF 2023
Still not sure which Heat Shrink Kit you want? Here are our top 3 Heat Shrink Kits from 2023.
 HS-4: Heavy Duty Heat Shrink Kit, Black #14 to #10
HS-4: Heavy Duty Heat Shrink Kit, Black #14 to #10
This heat shrink kit has 4 shrink tubes and 4 stakons. It has an Expanded I.D. or 0.4" and a Recovered I.D. of 0.15". Check it out here.
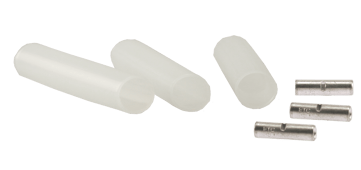 HSC-3: Heavy Duty Heat Shrink Kit, Clear #14 to #10
HSC-3: Heavy Duty Heat Shrink Kit, Clear #14 to #10
This heat shrink kit has 3 shrink tubes and 3 stakons. It has an Expanded I.D. of 0.4" and a Recovered I.D. of 0.15". Check it out here.
HSC-4: Heavy Duty Heat Shrink Kit, Clear #14 to #10
This heat shrink kit has 4 shrink tubes and 4 stakons. It has an Expanded I.D. of 0.4" and a Recovered I.D. of 0.15". Check it out here.
Conclusion
As you can see, there are many factors that go into choosing the best Heat Shrink Kit for you. The information above will help you to understand this product better so that you can pick the right Heat Shrink Kit for your application.
Click here to see all of Boshart’s Heat Shrink Kits.
Have further questions about this subject?

Head over to Boshart's Knowledge Base: technical product information, guidelines, and more.


![[Video] 3 Easy Solutions to Reduce Water Hammer](https://blog.boshart.com/hubfs/2022-08-15%20Fittings%202-48.jpg)


SHARE